Get in Touch
IBM Aspera Faspex critical vulnerability under active exploitation by IceFire operators
Target Industry
Indiscriminate, opportunistic targeting.
Overview
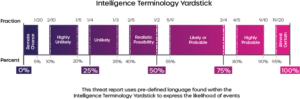
Severity level: Critical – Compromise will result in the loss of confidentiality and integrity of data in the first instance.
IBM has disclosed a critical vulnerability, being tracked as CVE-2022-47986 (CVSSv3 Score: 9.8.), a pre-authentication YAML deserialisation security flaw in Ruby on Rails code.
A Proof-of-Concept (PoC) code has been released in relation to the vulnerability which has been attributed to several attack campaigns, most notably that of the recent IceFire ransomware campaign.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2022-47986 would allow a remote threat actor to execute arbitrary code on the system, caused by a YAML deserialisation flaw. This is achieved by sending a specially crafted obsolete API call.
Vulnerability Detection
IBM has patched the vulnerability for the respective product version. As such, previous versions are vulnerable to potential exploit.
Affected Products
– Aspera Faspex 4.4.2 Patch Level 1 and below
Containment, Mitigations & Remediations
Due to the reported active exploitation of CVE-2022-47986, coupled with the fact that Aspera Faspex is typically installed on the network perimeter, administrators are strongly recommended to apply the Aspera Faspex 4.4.2 Patch Level 2 update as soon as possible.
Indicators of Compromise
Log files can be found in the ‘/opt/aspera/faspex/log’ folder. Log entries related to ‘PackageRelayController#relay_package’ have been classified as an Indicator of Compromise (IoC).
Threat Landscape
IBM Aspera has a significant portion of the Enterprise Application Integration market share. Threat actors generally utilise a combination of probability and asset value to determine which attack surfaces to focus on. As a result, the IBM Aspera products can emerge as prime targets. Due to the fact that enterprise applications have become an integral aspect of business operations, threat actors will continue to exploit vulnerabilities contained within such products in an attempt to extract the sensitive data contained therein.
Threat Group
The vulnerability was exploited in the recent IceFire ransomware campaign. IceFire ransomware emerged in March 2022, but the threat actors did not begin publishing exfiltrated victim data to their extortion site until August 2022.
IceFire operators have previously only targeted Windows systems, but their recent expansion to focus on Linux systems is a consistent trend that has been associated with additional ransomware groups such as Clop. Linux systems are typically server systems, which means that initial access techniques, such as phishing or drive-by compromise, are less effective as a method to gain access to these machines. Instead, threat actors are forced to rely on vulnerability exploitation which, while effective, diminishes a threat actor’s ability to launch widespread attacks.
Mitre Methodologies
Tactic:
TA0005 – Defence Evasion
Defence Evasion Technique:
T1070.002 – Indicator Removal: Clear Linux or Mac System Logs
Tactic:
TA0002 – Execution
Execution Technique:
T1053.003 – Scheduled Task/Job: Cron
Tactic:
TA0003 – Persistence
Persistence Techniques:
T1037.004 – Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts: RC Scripts
T1053.003 – Scheduled Task/Job: Cron
T1543.002 – Create or Modify System Process: System Service
Tactic:
TA0007– Discovery
Discovery Techniques:
T1082 – System Information Discovery
T1083 – File and Directory Discovery
Tactic:
TA0040 – Impact
Impact Techniques:
T1486 – Data Encrypted for Impact
T1489– Service Stop
Further Information